Introduction
Dendritic cells are professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs) that can capture and process tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) [1]. Given their ability to stimulate both adaptive and innate antitumor immune responses, DCs have been used as a powerful pharmacological tool for cancer immunotherapy [2].
These cells’ role is antigen presentation that is carried out through processing and presenting antigenic material to the T‐lymphocytes surface [3]. The main function of immature DCs is to take tumor‐derived components, while mature DCs affect the tumor‐reactive CD8+ CTLs and CD4+ T cells [4].
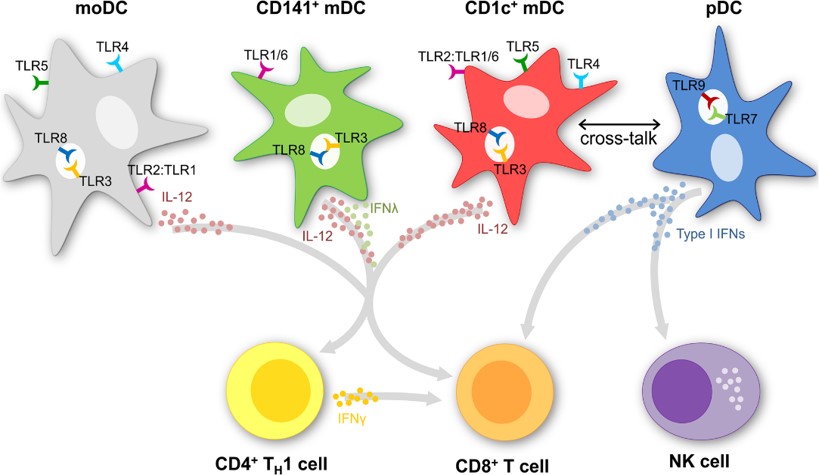
Figure 1: Dendritic cell subsets.
Dendritic cells can be differentiated from monocytes (moDC), which are often used in clinical trials because of their high yield. The naturally circulating dendritic cells can now also be enriched by immunomagnetic isolation. The naturally circulating dendritic cells can further be divided in myeloid (CD141+ and CD1c+ mDC) and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC). The subsets differ in function, localization, phenotype and cytokine production
Strategy
Depending on the type of DC-therapy used, long-term clinical efficacy upon DC-therapy remains restricted to a proportion of patients, likely due to lack of immunogenicity of tumor cells, presence of a stromal compartment, and the suppressive tumor microenvironment (TME), thereby leading to the development of resistance. In order to circumvent tumor-induced suppressive mechanisms and unleash the full potential of DC-therapy, considerable efforts have been made to combine DC-therapy with chemotherapy, radiotherapy or combine with another immunotherapy [5].
These combination strategies could enhance tumor immunogenicity, stimulate endogenous DCs following immunogenic cell death, improve infiltration of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) or specifically deplete immunosuppressive cells in the TME, such as regulatory T-cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells.
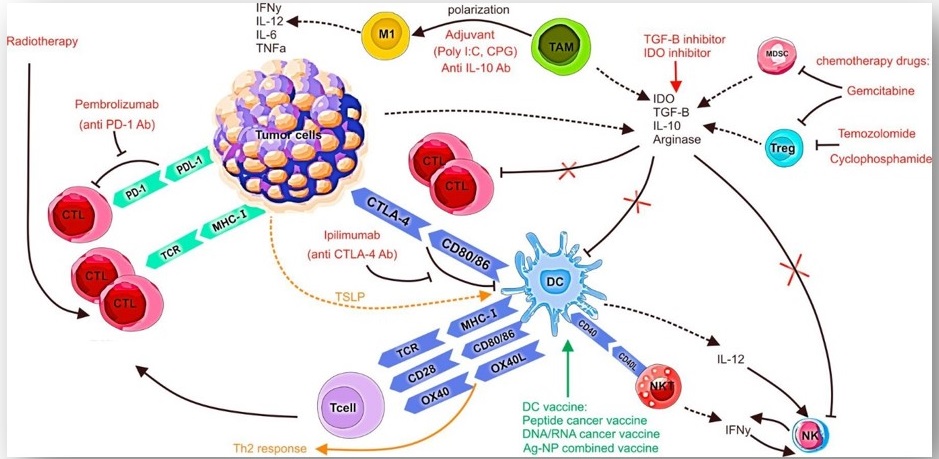
Figure 2: Immunological effects of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and checkpoint inhibitors.
Cyclophosphamide induces ICD which enhances the recruitment, activation, maturation, and antigen uptake by DCs.
Clinical Treatment
The picture of the right illustrates the production of DCs in the laboratory. The patient’s PBMC cells will be harvested by apheresis in hospital and appointed on-site local laboratory staff will transfer the PBMC sample to on-site local laboratory. In local laboratory center, they will prepare the PBMC isolation and then cryopreservation to send to Malaysia manufacturer. In Malaysia manufacturer, the cells are then cultured with IL-4 and GM-CSF. On day 5, immature DC (iDC) were pulsed with autologous tumor lysate plus keyhole limpet hemocyanin with addition of IL-4 and 25 ng/ml GM-CSF for 24 hours.
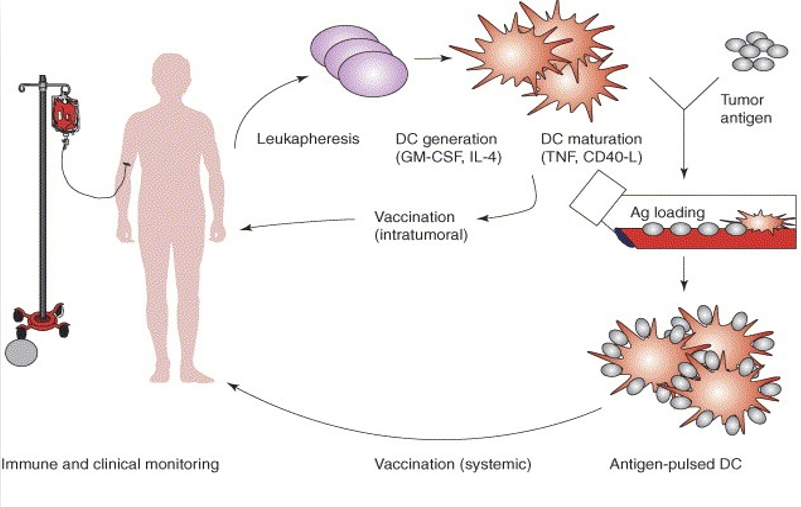
On day 6, antigen-loaded DC (aDC) were cultured with pro-inflammatory cytokine cocktail. After 24 hours, mature antigen-loaded DC (mDC, final product), were collected and frozen at the concentration of 5–6×106 viable cells/vial, and the final product of DCs will be calculated to the quantity of 1 ~ 2 x 107 dendritic cells per cycle use then suspended in 240mL normal saline. The cell products were tested according to the current Chinese Pharmacopoeia, such as microbial contamination testing being carried out to ensure the reliability, PCR based method for the mycoplasma detection to rule out contamination and quantification of bacterial endotoxin by kinetic turbidimetric methods. After passing the QC, the cell product will be cryopreserved and shipped to Hospital. After recovery in hospital, the cells are ready for infusion.
Cancer Types
In cooperation with the Tungs’ Taichung Metro Harbor Hospital, and various private hospitals in Malaysia, our group participated in application of various cell-therapies (DC, CIK, DC-CIK) in a variety of solid cancer treatment projects, that were approved by both the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Taiwan and the Ministry of Health of Malaysia.
The cell therapy applications include 22 types of stage 4 solid cancers, including: (1) breast cancer, (2) lung cancer, (3) colorectal cancer, (4) head and neck cancer, (5) esophageal cancer, (6) gastric cancer, (7) pancreatic cancer, (8) biliary tract cancer, (9) liver cancer, (10) kidney cancer, (11) bladder cancer, (12) prostate cancer, (13) ovarian cancer, (14) cervical cancer, (15) endometrial cancer, (16) germ cell cancer, (17) soft tissue sarcoma, (18) brain malignant tumor, (19) neuroendocrine cancer, (20) skin cancer, (21) thyroid cancer, (22) adrenal cancer. [ref: MOHW, Taiwan].
- Breast Cancer
- Lungs Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Head & Neck Cancer
- Esophageal Cancer
- Gastric Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Biliary Tract Cancer
- Liver Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Endometrial Cancer
- Germ Cell Cancer
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Brain Malignant Tumor
- Neuroendocrine Cancer
- Skin Cancer
- Thyroid Cancer
- Adrenal Cancer
In cooperation with the Tungs’ Taichung Metro Harbor Hospital, and various private hospitals in Malaysia, our group participated in application of various cell-therapies (DC, CIK, DC-CIK) in a variety of solid cancer treatment projects, that were approved by both the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Taiwan and the Ministry of Health of Malaysia.
The cell therapy applications include 22 types of stage 4 solid cancers, including the cancer types listed in the table below [ref: MOHW, Taiwan].
- Adrenal Cancer
- Biliary Tract Cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Brain Malignant Tumor
- Breast Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Endometrial Cancer
- Esophageal Cancer
- Gastric Cancer
- Germ Cell Cancer
- Head & Neck Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Liver Cancer
- Lungs Cancer
- Neuroendocrine Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Skin Cancer
- Thyroid Cancer
Treatment Flow
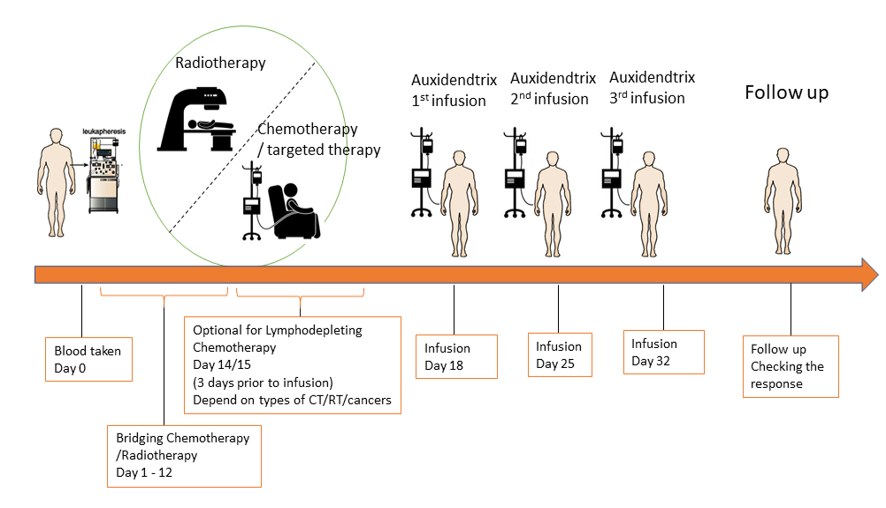
Infusion

For autologous use only. Patients will receive at least 3 cycles of DCs infusion with one-week intervals between each cycle. 1~2 x107 cells were suspended in 100mL normal saline and administered via intravenous infusion within 20 minutes.
The immune cell therapy program can be combined with other treatment methods, including anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) and antipyretic analgesics to relieve the patient’s discomfort. Or combined use of radiation therapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, and so on to improve the overall anti-cancer efficacy. All concomitant treatment methods must be evaluated by the operating specialist’s professional clinical experience, and the relevant adverse reactions of concomitant treatment should be observed at any time.
All patients were followed up after discharge, including blood routine examination and PET CT/CT screening every 3 months for the first 2 years, 6 months for the next 3 years, and yearly thereafter from the fifth year.
Possible Side Effects
According to the results of clinical trial literature, the most common adverse reactions of CIK cell therapy are mostly mild symptoms such as fever and pain. Although the frequency is incredibly low, the symptoms will resolve spontaneously without treatment. However, each patient may have special reactions (idiosyncrasy) due to individual differences and special constitutions. If nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or shock occurs after the cell reinfusion, the cell reinfusion should be stopped and treated according to the specialist’s instructions.
| Adverse Effect | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Grade 1 | The operating physician needs to place the patient in a comfortable space and observe until the adverse event resolves spontaneously or gives appropriate physical support (ice compress, drinking warm water, sleep, etc.). |
| Grade 2 | The operating physician immediately places the patient and observes whether the adverse event tends to ease or become more serious. If it tends to be relieved, physical support is given to accelerate the resolution of the adverse event; if it tends to be serious, evaluate the severity of the patient and give appropriate drug support (antipyretic, analgesic, steroid, etc.). Continue observation and drug support until the adverse event stabilizes or resolves. Suspend this course of treatment and enter the observation period and reassess whether to continue treatment after the cause is found out. |
| Grade 3 | The operating physician must immediately take emergency measures and administer medication support (antipyretic, analgesic, steroids, pressure boosters, electrolyte infusion… etc.) according to the patient’s symptoms. Arrange to be hospitalized and continue treatment and slow medication reduction until the symptoms are completely resolved. The patient withdraws from this course of treatment, terminates the cell reinfusion, and arranges for routine medical care for the patient. |
| Grade 4 | The operating physician must immediately be sent to the emergency department to take first aid measures and provide life support (intratracheal intubation, steroids, pressure boosters, electrolyte infusion, etc.) according to the patient’s symptoms. Arrange to the intensive care unit as soon as possible and continue treatment until the symptoms are completely stable or resolved. The patient withdraws from this course of treatment, terminates the cell reinfusion, and arranges for routine medical care for the patient. |
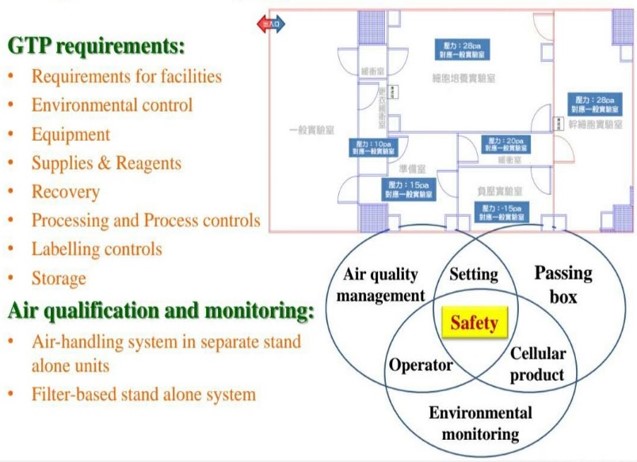
Top GTP Laboratory

The facility is designed with regulations that are stricter than any Good Tissue Laboratory (GTP) regulations to avoid risks of environmental contamination including multiple gowning procedures (primary and secondary changing rooms, biologically safety areas, and limited access to qualified persons. The facility complies with the FDA high standard secondary dressing facility.

SITE SPECIFICATIONS
It has a cleanliness level of 10,000, a “positive pressure, constant humidity, constant temperature” high-standard dust-free independent laboratory, and a complete control mechanism, which can provide various process facilities for cell therapy.
CLEANLINESS
With a cleanliness of 10,000 and a complete control mechanisms, it can provide various process facilities required for cell therapy.
STRICT REQUIREMENTS
Adhere to the use of high-quality manufacturer-sourced reagents, high-end equipment, and full-process serum-free culture to improve the effectiveness and safety of human cell tissue operations. Strict operation procedures, manufacturing procedures, storage conditions, effective time and records are established for the acceptance/feeding of human cell tissues, acceptance or return, distribution, and destruction or disposal.



Comprehensive Support
- Patient Educational Materials
- Doctor’s Educational Materials
- Free Pre-treatment Assessment
- Comprehensive Auxiliary support for treatments in Malaysia
- Post Treatment Monitoring
Additional Reading
Presentations
Scientific Publications
Vamos life-cell therapies
The Vamos group of companies is engaged in life-cell therapies since 2016. We provide cutting-edge biotechnology products to both hospitals and patients seeking the most effective cancer treatments. Our suite of T-cell based immunotherapies and services are highly accurate, personalized, and focused on providing the most effective treatments based on highest quality standards and at the lowest cost possible.
Vamos Services
Our group provides the following services:
- Production and supply of autologous CAR-T cells for CAR-T treatments provided by hospitals in Malaysia and internationally.
- Medical tourism and auxiliary services related to hosting of international patients taking CAR-T treatments in Malaysia.
Facts about Vamos
- Our group is the only provider of CAR-T therapy in Malaysia for blood cancers.
- Our CAR-T therapy is approved by the Malaysian Ministry of Health.
- All patients that participated in the clinical trial achieved complete remission are live a life free of cancer (with exception of 3 patients that passed away before receiving the actual CAR-T treatment).
- 6 of the top hospitals in Malaysia provide CAR-T treatments with our products.
- So far, we have treated more than 100 number of patients with stage 4 cancer, and the success rate of our CAR-T therapy is over 90%.
- Up to date, all patients treated with our CAR-T therapy have been treated successfully and without experienced any severe side effects.
- The quality of our CAR-T therapy is second to none, while the cost of our therapy is possibly the lowest cost in healthcare worldwide.
- In addition to CAR-T therapy (for both blood and solid cancers), we also provide DC therapy, CIK therapy, and DC-CIK therapy for solid cancers. Together with our clinical trial partner hospital, our group has conducted more than 2,000 DC, CIK & DC-CIK treatments.

References
- Banchereau J, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature (1998) 392(6673):245–52. doi:10.1038/32588
- Anguille S, Smits EL, Bryant C, Van Acker HH, Goossens H, Lion E, et al. Dendritic cells as pharmacological tools for cancer immunotherapy. Pharmacol Rev (2015) 67(4):731–53. doi:10.1124/pr.114.009456
- Steinman RM, Banchereau J. Taking dendritic cells into medicine. Nature. 2007;449:419‐426.Schmidt TL, Negrin RS, Contag CH. A killer choice for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Res (2014) 58(2–3):300–6. doi:10.1007/s12026-014-8507-2
- Rosenberg SA. Cancer vaccines based on the identification of genes encoding cancer regression antigens. Immunol Today. 1997;18:175‐182.
- van Gulijk M, Dammeijer F, Aerts JGJV and Vroman H (2018) Combination Strategies to Optimize Efficacy of Dendritic Cell-Based Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 9:2759. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02759
